
There is visible jaundice (yellowish coloration of the skin and mucous membranes) and pain in the abdomen's upper right quarter. The second phase encompasses a period usually from the first to the third day of the intoxication.The patient might experience weakness, nausea, and vomiting.
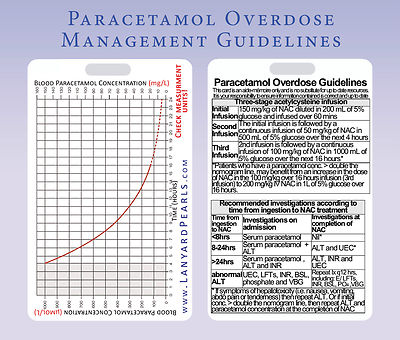
 First phase occurs in the first 24 hours after toxic dose ingestion. There are four stages of paracetamol poisoning: The phases are only accurate if NAC, or at least an alternative to N-acetylcysteine, is not administered quickly. Fortunately, that's simple:Īcetaminophen poisoning stages include four phases of developing liver failure. In the intravenous route case, you also must consider how much diluent to use. Keep in mind that the maximum dose to give to any patient intravenously is as if they weighed 110 kg, meaning maximum doses, consecutively, of 16500 mg, 5500 mg, and 1100 mg. To count the first dose, you have to multiply the patient's weight in kg by 150 mgįor the second dose, multiply the patient's weight in kg by 50 mgįor the third (last dose), multiply the patient's weight in kg by 100 mg To count the first dose of NAC given p.o., you have to multiply the patient's weight in kg (kilograms) by 140 mg.įor the second and consecutive doses, you have to multiply the patient's weight in kg by 70 mg. To calculate the amount of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to administer to the patient, you first have to know their weight and route of administration (oral or intravenous). Two actions combined give us a bigger chance to save our liver cells from the toxic NAPQI. It forces more paracetamol molecules to follow the conjugation pathway. It is a substrate for the glutathione production - which can give us more glutathione and more neutralizing possibilities,. What is NAC for Tylenol overdose? It works in two ways: That's why the main consequence of paracetamol overdose is liver failure. Being unable to neutralize all the deadly NAPQI molecules, we're prone to its damaging properties. Here comes the problem, as we only have limited glutathione storage. When there is too much acetaminophen, more substance follows the oxidation pathway, producing more toxic NAPQI. NAPQI is conjugated and excreted with urine. Luckily, we have a mechanism for neutralizing NAPQI using a glutathione molecule. It can cause liver necrosis (death of the liver cells). Oxidation leads to the production of a small amount of a toxic metabolite, NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine). Most of the paracetamol breakdown happens with the process of conjugation (95% of it). When you take Tylenol in regular, therapeutic doses, the substance is processed by two mechanisms.
First phase occurs in the first 24 hours after toxic dose ingestion. There are four stages of paracetamol poisoning: The phases are only accurate if NAC, or at least an alternative to N-acetylcysteine, is not administered quickly. Fortunately, that's simple:Īcetaminophen poisoning stages include four phases of developing liver failure. In the intravenous route case, you also must consider how much diluent to use. Keep in mind that the maximum dose to give to any patient intravenously is as if they weighed 110 kg, meaning maximum doses, consecutively, of 16500 mg, 5500 mg, and 1100 mg. To count the first dose, you have to multiply the patient's weight in kg by 150 mgįor the second dose, multiply the patient's weight in kg by 50 mgįor the third (last dose), multiply the patient's weight in kg by 100 mg To count the first dose of NAC given p.o., you have to multiply the patient's weight in kg (kilograms) by 140 mg.įor the second and consecutive doses, you have to multiply the patient's weight in kg by 70 mg. To calculate the amount of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to administer to the patient, you first have to know their weight and route of administration (oral or intravenous). Two actions combined give us a bigger chance to save our liver cells from the toxic NAPQI. It forces more paracetamol molecules to follow the conjugation pathway. It is a substrate for the glutathione production - which can give us more glutathione and more neutralizing possibilities,. What is NAC for Tylenol overdose? It works in two ways: That's why the main consequence of paracetamol overdose is liver failure. Being unable to neutralize all the deadly NAPQI molecules, we're prone to its damaging properties. Here comes the problem, as we only have limited glutathione storage. When there is too much acetaminophen, more substance follows the oxidation pathway, producing more toxic NAPQI. NAPQI is conjugated and excreted with urine. Luckily, we have a mechanism for neutralizing NAPQI using a glutathione molecule. It can cause liver necrosis (death of the liver cells). Oxidation leads to the production of a small amount of a toxic metabolite, NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine). Most of the paracetamol breakdown happens with the process of conjugation (95% of it). When you take Tylenol in regular, therapeutic doses, the substance is processed by two mechanisms.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
